Tesla Motors Japan LLC announced that Megapack will be introduced to an energy storage facility in Hokkaido, Japan. The announcement on 19th of August 2021 claimed the facility has an output of 1523.8kW (capacity 6052.2kWh) and is scheduled to start operations in summer 2022.
Original post in Japanese: テスラが北海道に日本初の『蓄電池発電所」開設を発表〜再エネ導入拡大を加速by Ryuichi Kino on EVsmart Blog
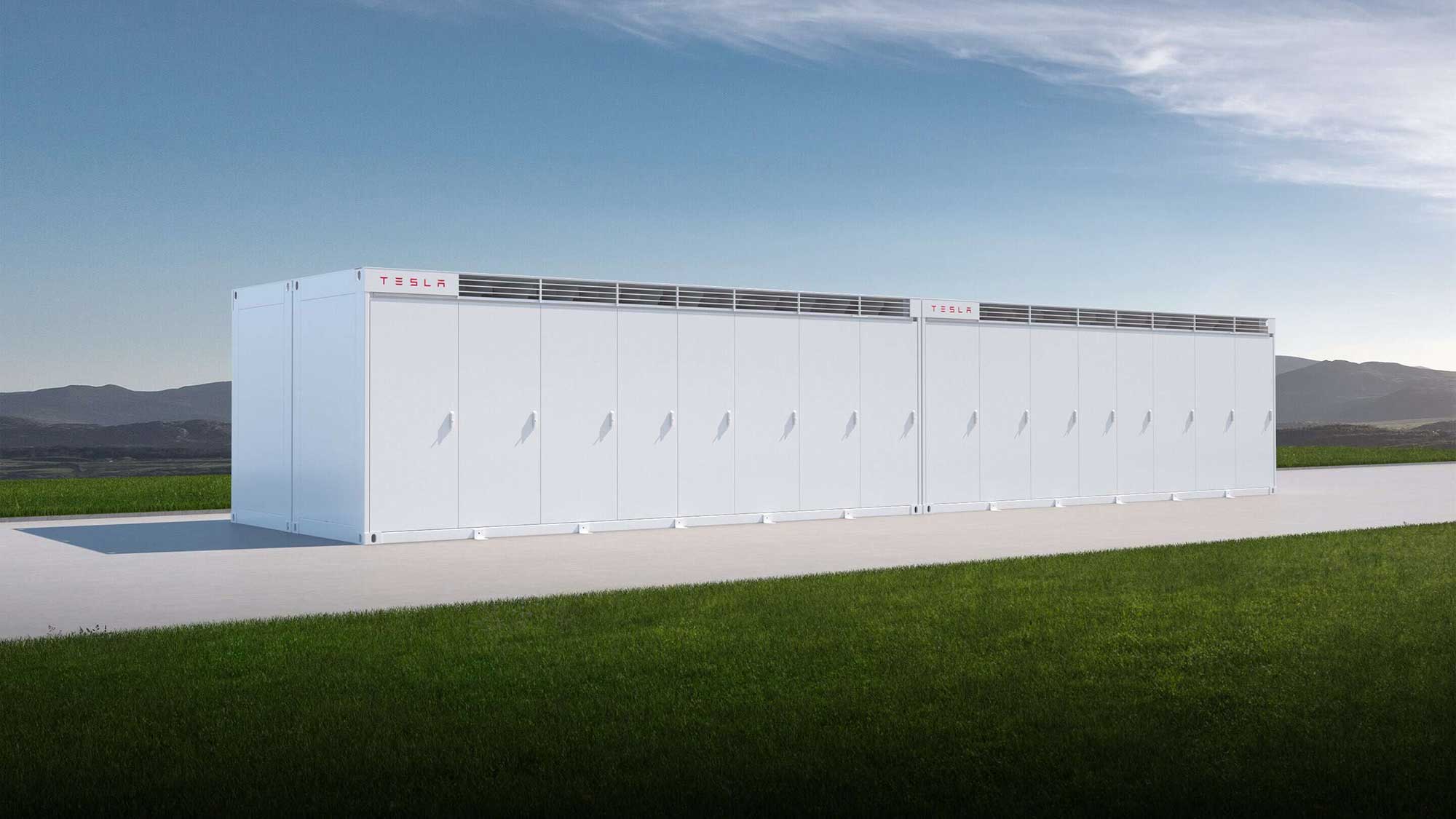
A first Megapack facility in Japan
Located in the Hokkaido Chitose Battery Power Park, it will the first energy storage system to be connected to Japan’s grid and wholesale electricity market directly, where previous such systems have only been linked with power plants. Tesla Japan is confident the wholesale electricity and balancing market will expand in Japan, and further Megapack facilities will emerge in the future.

©Tesla, Inc.
This facility will be constructed by two domestic companies with experience in renewable and clean energy, Global Engineering and Ene Vision. Global Engineering describes its role as an aggregator company, aiming to expand renewable energy usage nationwide while also optimising the various advantages of Megapack; large capacity, guaranteed energy characteristics, 24 hours surveillance and network control.
Large facilities scheduled to start operating late this year
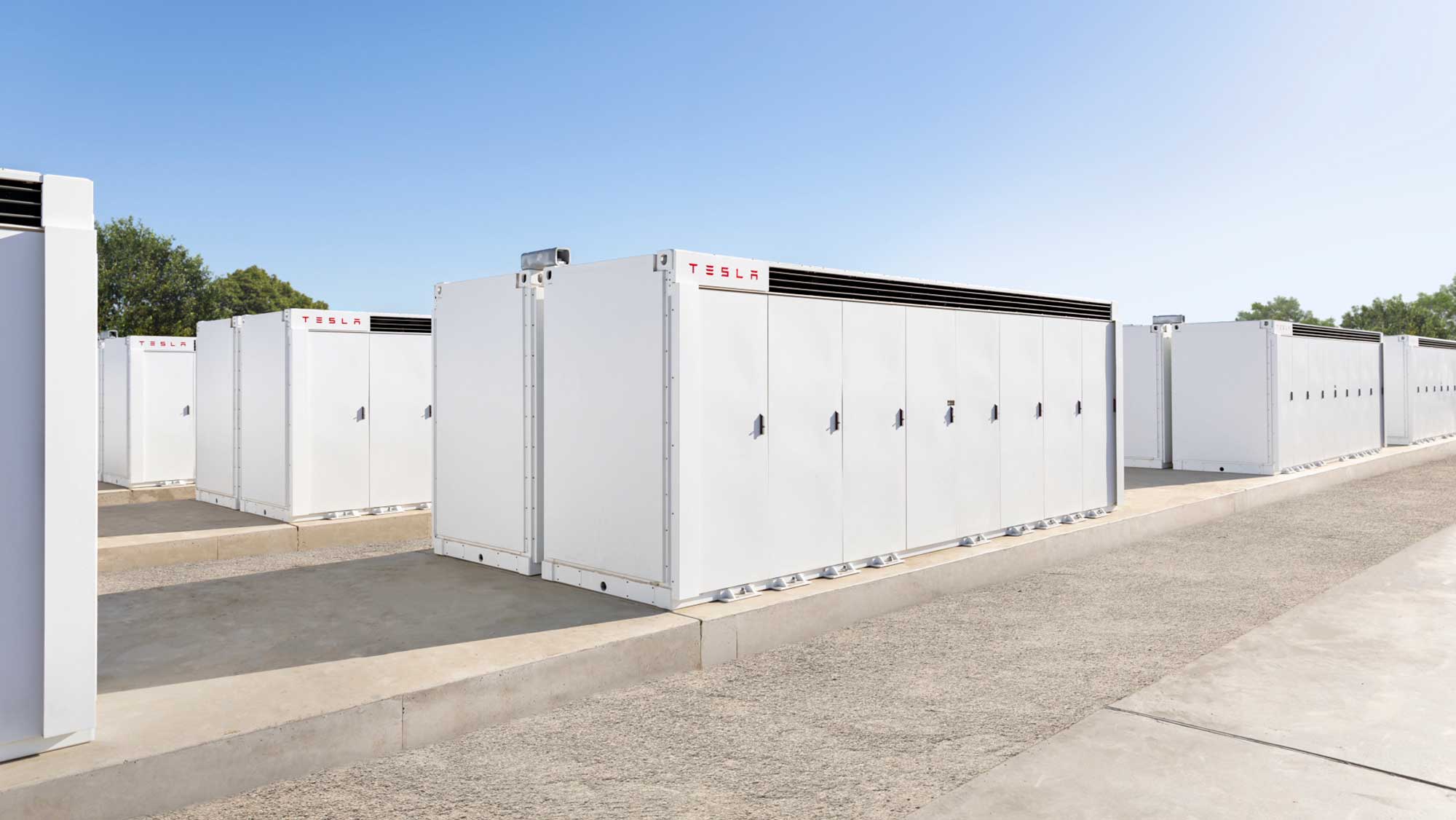
More than just a collection of batteries, the Megapack system includes thermal control regulators, power conditioners, software, testing and ongoing customer service. Indeed, Tesla emphasizes the ease with which Megapack can be installed, and a scalability based on modules with maximum output 771.4kW and maximum capacity 3085kWh.
In Moss Landing, California, a huge 183MW (730MWh) facility is being constructed by Pacific Gas and Electric, while a 300MW (450MWh) is also making news in Geelong, Australia. A second Megapack in Japan is expected to be located Tsukubamirai, Ibaraki with capacity of 3MWh and constructed by Takasago Thermal Engineering CO., Ltd.
Despite these efforts, Tesla, amongst many other companies, is struggling to secure its supply of batteries. Nikkei online reported that the Hokkaido Megapack will obtain batteries from China’s CATL, with whom Tesla has a supplier contract and whose batteries are currently employed in Model 3s for the Asian market. With CATL as supplier, transport costs to Japan are reduced, and the lower density of their Iron phosphate batteries are ideal for stationary storage facilities, as compared to Lithium Ion batteries.
EV and power plant refurbishment need to be carried out simultaneously

©Tesla, Inc.
The introduction of large scale storage systems like Megapack to Japan will provide relief to a country with a poor record in using renewable energy. Despite a commitment to the Paris agreement, Japan lacks a clear vision to reduce its heavy dependence on imported coal. Poor infrastructure means existing renewable energy companies often face harsh criticism on the multiple occasions they have been forced to restrict supply to their customers, such as Kyushu Electric Power as recently as May 2021.
Our EVsmart blog advocates EVs as a means to reduce CO2 emissions, but we are keenly aware it is not a magic bullet. The slow but gradual adoption of EVs must be matched with expanded infrastructure. Unfortunately, the situation in Japan over the last 3 decades is one of stagnation, and this is reflected in comments by the public, many of which continue to argue the environmental impact of EVs during their production, rather than their potential.
The introduction of Megapack, and other such systems, raises hope of a sustainable and scalable infrastructure to support and encourage Japan’s adoption of renewable energy, EVs and the goals of the Paris agreement.
(Author: Ryuichi Kino, Translator: Meiko Sugita)












コメント